python包之-seaborn可视化
Seaborn是一个很棒的可视化库,尤其是当数据维度很大的时候,Seaborn可以让我们用最少的代码去绘制一些描述性统计的图,便于找寻各维度变量之间的特征,本篇我们将会利用科赛上Iris鸢尾花数据集。对Stripplot & Swarmplot, Boxplot & Violinplot, Barplot & Pointplot,以及抽象化的Factorplot,为大家进行讲解。
Iris鸢尾花数据集:Iris数据集是常用的分类实验数据集,由Fisher, 1936收集整理。“Iris也称鸢尾花卉数据集,是一类多重变量分析的数据集。数据集包含150个数据集,分为3类,每类50个数据,每个数据包含4个属性。可通过花萼长度(sepal_length),花萼宽度(sepal_width),花瓣长度(petal_length),花瓣宽度(petal_width)4个属性预测鸢尾花卉属于(Setosa,Versicolour,Virginica)三个种类中的哪一类”。
导入库
import warnings warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline import seaborn as sns
Stripplot
Stripplot的本质就是把数据集中具有Quantitative属性的变量按照类别去做散点图(Scatterplot)。
我们将纸鸢花数据集中不同种类花的Sepal Length做Stripplot可视化。
plt.figure(1,figsize=(12,6)) plt.subplot(1,2,1) sns.stripplot(x='species',y='sepal_length',data=iris) #stripplot plt.title('Striplot of sepal length of Iris species')with sns.axes_style("whitegrid"): # 这个是临时设置样式的命令,如果不写,则按默认格式'darkgrid'进行绘制 plt.subplot(1,2,2) plt.title('Striplot of sepal length of Iris species') sns.stripplot(x='species',y='sepal_length',data=iris,jitter=True) # jitterplot plt.show()
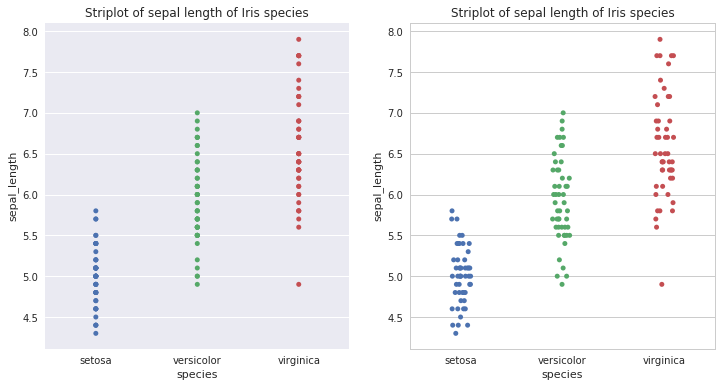
上边左侧的图片便是在默认风格下用Stripplot绘制的散点图。在很多情况下,Stripplot中的点会重叠,使得我们不容易看出点的分布情况。一个简单的解决办法就是用在Stripplot的基础上绘制抖动图(jitterplot),仅沿着类别坐标轴的方向去随机微调整点的位置,显示出分布情况。
Swarmplot
另一个解决Stripplot中点重叠的办法就是绘制Swarmplot,它的本质就是用通过算法,在类别坐标轴的方向上去‘延展’绘制这些原本重合的点。 我们将纸鸢花数据集中不同种类花的Petal Length和Petal width做Swarmplot可视化。
plt.figure(1,figsize=(12,6)) plt.subplot(1,2,1) sns.swarmplot(x='species',y='petal_length',data=iris) with sns.axes_style("ticks"): # 这次使用了ticks风格 plt.subplot(1,2,2) sns.swarmplot(x='species',y='petal_width',data=iris) plt.show()
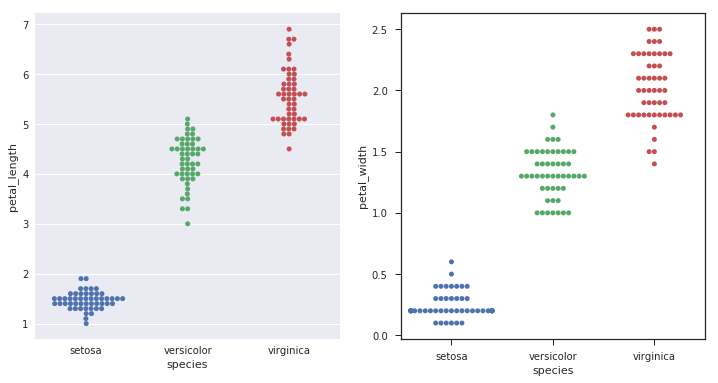
Boxplot
箱形图,主要包含六个数据节点,将一组数据从大到小排列,分别计算出上边缘,上四分位数Q3,中位数,下四分位数Q1,下边缘,还有异常值。 下面将纸鸢花数据集中的四个变量sepal_length, sepal_width, petal_length和petal_width做箱形图可视化。
var = ['sepal_length','sepal_width','petal_length','petal_width'] axes_style = ['ticks','white','whitegrid', 'dark'] fig = plt.figure(1,figsize=(12,12))for i in range(4): with sns.axes_style(axes_style[i]): # 将除了默认的darkgrid之外的样式都展现一遍 plt.subplot(2,2,i+1) sns.boxplot(x='species',y=var[i],data=iris) plt.show()
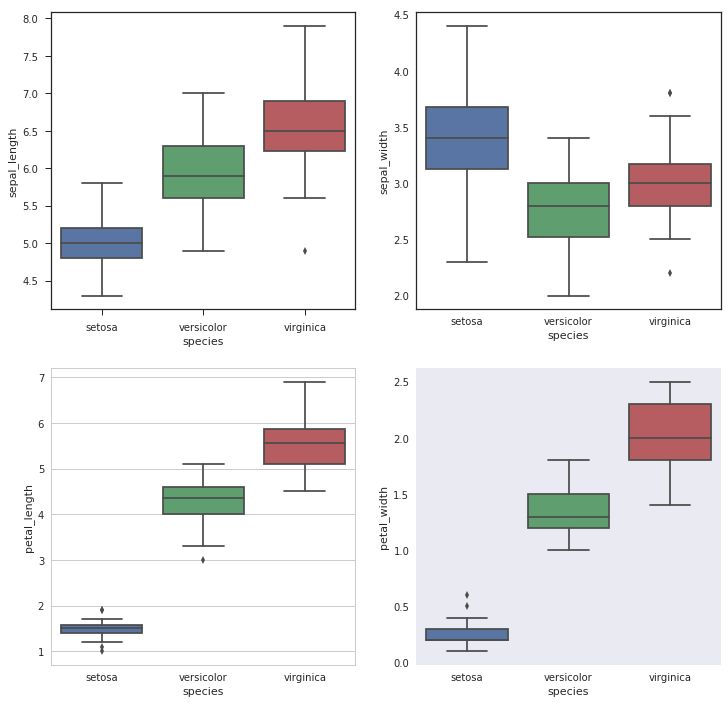
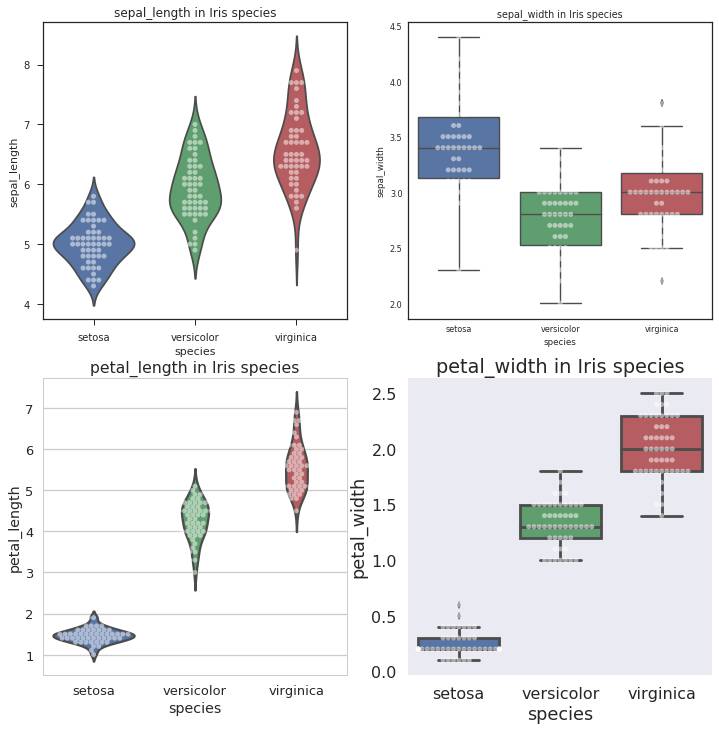
Violinplot
Violinplot相当于结合了箱形图与核密度图,更好地展现出数据的量化形态。
context= ['notebook','paper','talk','poster'] axes_style = ['ticks','white','whitegrid', 'dark'] plt.figure(1,figsize=(12,12))for i in range(4): with sns.axes_style(axes_style[i]):#设置axes_style sns.set_context(context[i]) # 设置context style,默认为notebook,除此之外还有paper,talk,poster plt.subplot(2,2,i+1) plt.title(str(var[i])+ ' in Iris species') sns.violinplot(x='species',y=var[i],data=iris) plt.show()
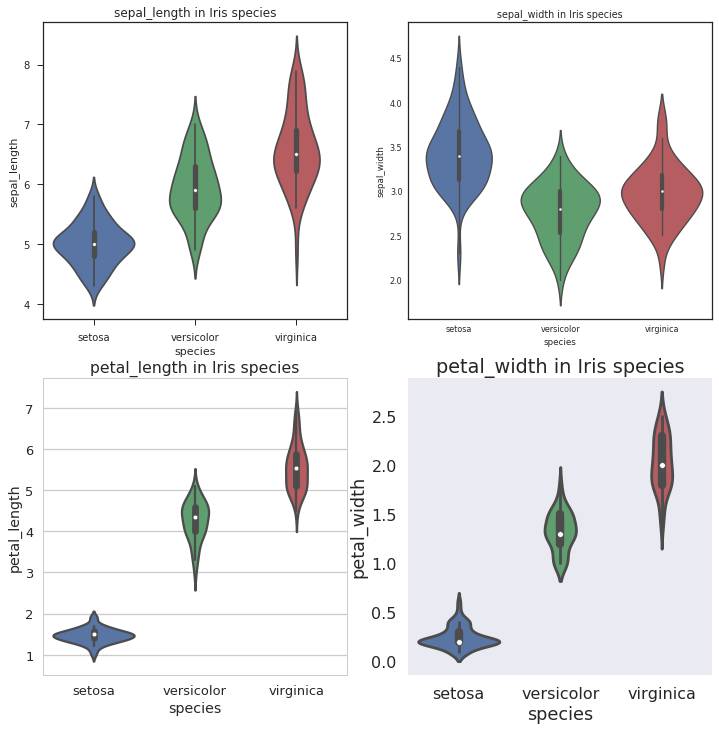
Violinplot用Kernel Density Estimate去更好地描述了quantitative变量的分布。
与此同时,也可以组合Swarmplot和Boxplot或Violinplot去描述Quantitative变量。用鸢尾花数据集展示如下:
context= ['notebook','paper','talk','poster'] axes_style = ['ticks','white','whitegrid', 'dark'] plt.figure(1,figsize=(12,12))for i in range(4): with sns.axes_style(axes_style[i]):#设置axes_style sns.set_context(context[i])#设置context plt.subplot(2,2,i+1) plt.title(str(var[i])+ ' in Iris species') sns.swarmplot(x='species', y=var[i], data=iris, color="w", alpha=.5) sns.violinplot(x='species', y=var[i], data=iris, inner=None) if i%2 ==0 else sns.boxplot(x='species', y=var[i], data=iris) # 分别用swarmplot+violinplot 和swarmplot + boxplot plt.show()
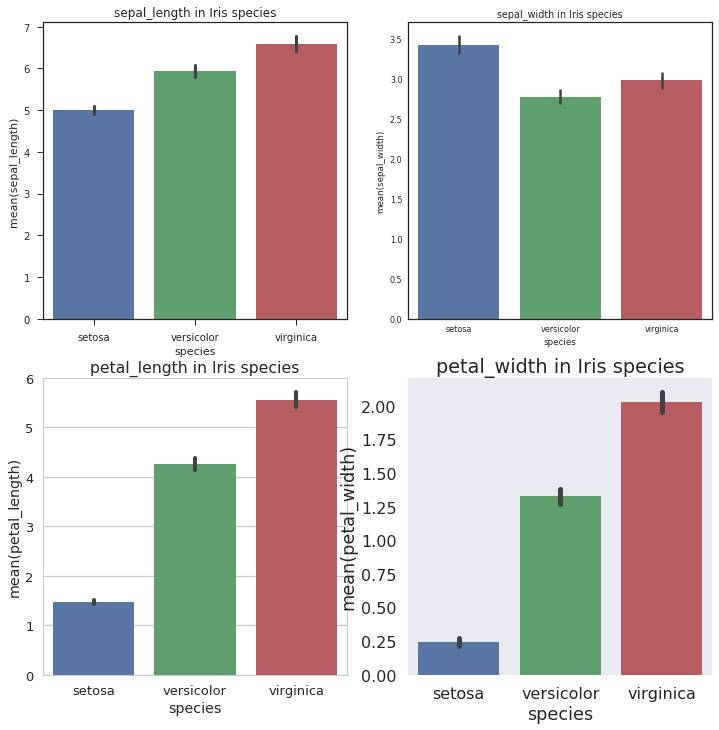
Barplot
Barplot主要是展现在分类中的Quantitative变量的平均值情况,并且用了Boostrapping算法计算了估计值的置信区间和Error bar.用鸢尾花数据集。
plt.figure(1,figsize=(12,12))for i in range(4): with sns.axes_style(axes_style[i]):#设置axes_style sns.set_context(context[i]) # 设置context style,默认为notebook,除此之外还有paper,talk,poster plt.subplot(2,2,i+1) plt.title(str(var[i])+ ' in Iris species') sns.barplot(x='species',y=var[i],data=iris) plt.show()
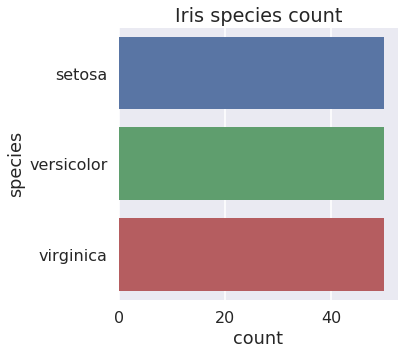
Countplot
如果想知道在每个类别下面有多少个观察值,用Countplot就可以,相当于是做一个Observation Counts,用鸢尾花数据集展示如下:
plt.figure(figsize=(5,5)) sns.countplot(y="species", data=iris) # 设置y='species',将countplot水平放置 plt.title('Iris species count') plt.show()
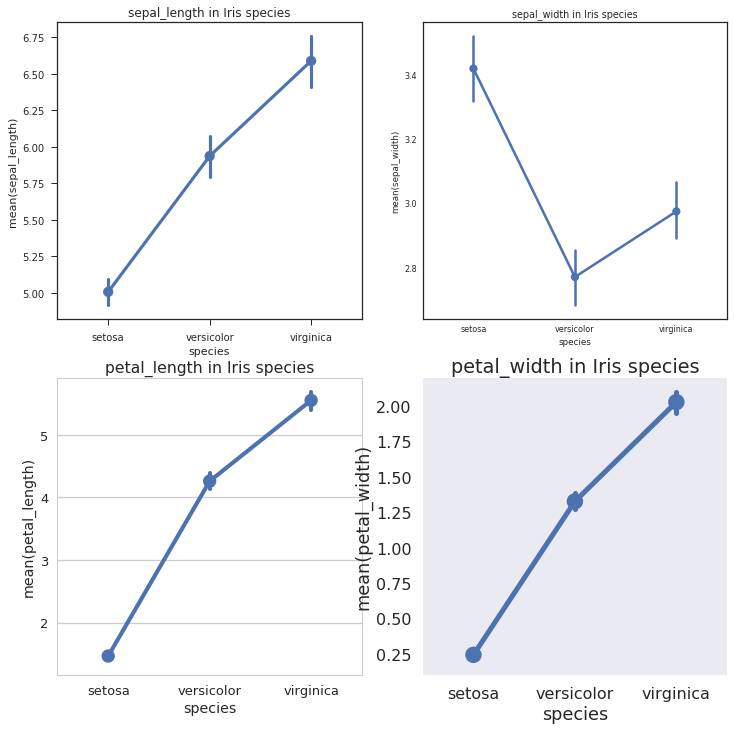
Pointplot
Pointplot相当于是对Barplot做了一个横向延伸,一方面,用Point Estimate和Confidence Level去展示Barplot的内容;另一方面,当每一个主类别下面有更细分的Sub-Category的时候,Pointplot可以便于观察不同Sub-Category在各主类别之间的联系。展示如下:
plt.figure(1,figsize=(12,12))for i in range(4): with sns.axes_style(axes_style[i]):#设置axes_style sns.set_context(context[i]) # 设置context style,默认为notebook,除此之外还有paper,talk,poster plt.subplot(2,2,i+1) plt.title(str(var[i])+ ' in Iris species') sns.pointplot(x='species',y=var[i],data=iris) plt.show()
Factorplot
Factorplot可以说是Seaborn做Category Visualization的精髓,前面讲的这些Plot都可以说是Factorplot的具体展示。我们可以用PariGrid去实现对多个类别的数值特征用同一种Plot做可视化。
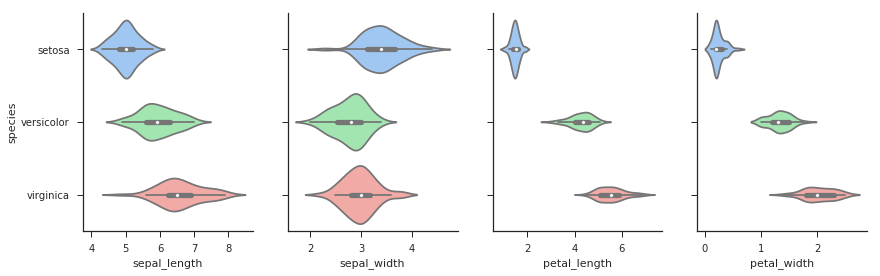
sns.set(style="ticks") g = sns.PairGrid(iris, x_vars = ['sepal_length','sepal_width','petal_length','petal_width'], y_vars = 'species', aspect=0.75,size=4) # 设置间距和图片大小 g.map(sns.violinplot,palette='pastel') plt.show()
在这个数据集中,Quantitative的变量主要有房屋的面积Area,每平米单价Price,以及房屋总价Tprice。
博客地址:http://blog.yoqi.me/archives/4034
这篇文章还没有评论